“If you want to change the world, start with yourself.”
Mahatma Gandhi
ISO 14001 Certification
Mahatma Gandhi’s wisdom can be applied to achieving ISO 14001 certification. There are more than 300,000 organizations certified to ISO 14001 worldwide. With every single certification, we get closer to environmental integrity and advance our mutual goals of protecting our planet and its valuable resources.
In addition to helping the world, ISO 14001 certification offers many other benefits to an organization. By addressing the risks and opportunities directly related to your environmental impact, you position your company to meet and exceed the standards and demands of potential new clients and stockholders, increasing its potential for growth and profitability. Everybody wins.
This article discusses multiple aspects of ISO 14001 including your Environmental Management System (EMS), the benefits of certification, the process approach, the context and scope of the organization, and the relationship between ISO 9001 and ISO 14001.
Manage Environmental Responsibilities
Like all ISO standards, 14001 follows the principles of action for improvement, management commitment, and company-wide involvement regardless of business size. More a set of tools than a set of regulations, the 14001 standard allows companies to manage their environmental responsibilities within the plan-do-check-act approach that is familiar to ISO compliance.
Developed by the ISO Technical Committee ISO/TC 207, ISO 14001 and its supporting standards focus on systems that address internal and external audits, communication, life-cycle analysis and labeling, and environmental challenges. It sets criteria and framework that organizations can follow to set up an effective Environmental Management System (EMS) which can be used by companies of any size in any industry.
Compliance, and eventual certification, serve as proof to current and potential customers, suppliers, and stakeholders that the impact the company has on the environment (no matter how small) is being consistently measured and improved upon.

Evaluate Environmental Impacts
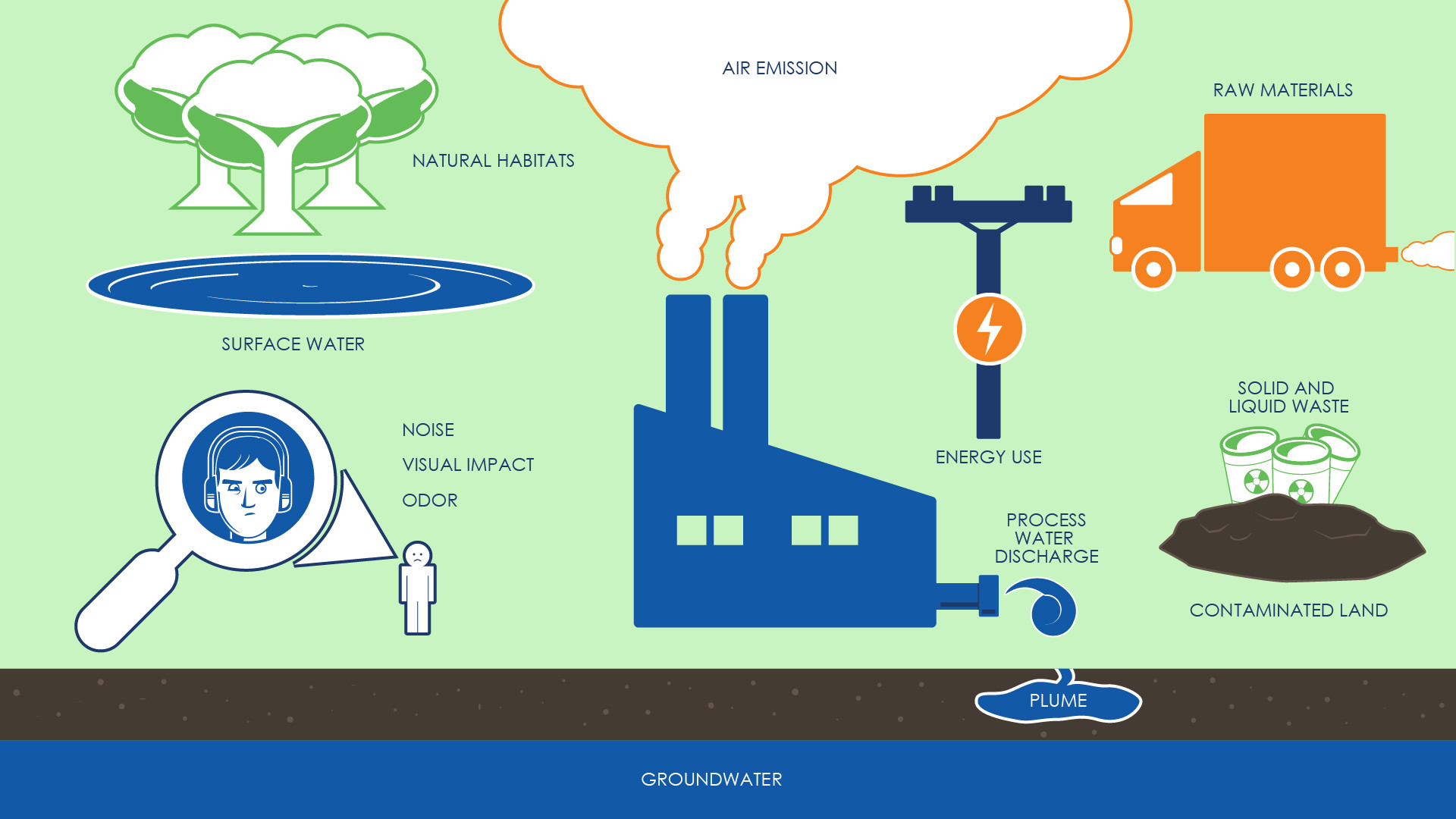
Organizations will evaluate how aspects of their business impact the surrounding environment and may examine operations, waste management, air, water, and soil contamination, climate change impact, and efficiency.
By proactively managing the risks and opportunities associated with its environmental footprint, the company positions itself to not only meet but also surpass the expectations of potential new clients. This strategic approach enhances the company’s brand and potential for both growth and profitability.
What are the Benefits of ISO 14001 Certification?
Choosing to work toward ISO 14001 compliance is often a decision made from necessity to comply with a potential customer’s requirements. However, the benefits a business can gain from implementation prove that the work put into ISO 14001 compliance can be for more than just contract satisfaction.
Often, when the topic of environmental impact makes headlines, stories are tied to large, multinational corporations. To demonstrate to stakeholders that they are doing everything in their power to minimize their impact, these organizations find ISO 14001 certification to be highly valuable and worth paying attention to.
ISO 14001 and Small Businesses
For smaller organizations, it’s surprising to find that the benefit of implementing the standard exceeds that realized by larger organizations. With ISO 14001 certification, smaller companies see improved environmental performance, win new contracts, eliminate waste, and improve efficiencies that significantly improve growth. In addition, smaller companies can demonstrate to their teams, suppliers, customers, and investors they have taken their responsibility to the planet seriously.
By addressing a wide array of areas impacted by environmental excellence, companies can decisively evaluate how their organization may find growth through compliance and certification. From improved professional relationships, regulations and legal compliance, increased profitability, process and change management, and company-wide communication, businesses of all sizes will benefit from implementing the ISO 14001 standard for excellence.
Improved Professional Relationships
Regardless of whether a contract mandates ISO 14001 certification, demonstrating the time and effort invested in ensuring compliance with these rigorous standards reassures stakeholders that companies are committed to upholding high-quality practices, proving their dedication to doing things right.
It isn’t just about customers. Suppliers, employees, investors, and even the local community will be affected by the impact companies make on the environment. As the attention of the general consumer population becomes more and more focused on environmental impact, organizations need to be prepared to answer the ever-more-stringent call for excellence.
Demonstrating this excellence through a meticulously structured and consistently monitored Environmental Management System (EMS) instills trust by ensuring a reliable measurement of a company’s impact. It not only enables ongoing efforts for improvement even after companies achieve certification standards but also initiates a positive domino effect for partnerships with suppliers, who are required to meet these benchmarks.

Regulations and Legal Compliance
The number of environmental regulations placed on companies in all sectors increases every day. ISO 14001 lays out a framework that helps organizations identify and track compliance with requirements that apply to their business. They are able to monitor changes associated with environmental impact and lay out plans to remain compliant in order to satisfy all legal obligations and regulatory requirements.
Increased Profitability
Reduction of cost isn’t a benefit that is as obvious to companies pursuing ISO 14001 compliance, but an EMS can play a large role in increased profitability driven by reduced spending. Using the system to keep track of energy and resources spent to create deliverables naturally results in improved efficiency and reduction in spending on energy and materials. By eliminating waste, reducing consumables, and saving on energy, bottom lines skyrocket.
Moreover, some companies will benefit from the elimination of environmental incidents that result in fines, cleanups, repairs, and other liabilities.
All of this will result in the ability to improve financial advantage over competitors – less cost results in a more affordable product, and customers will take notice.
Process and Change Management
As with all ISO compliance, a large focus of implementing this system will be on process improvement and managing change. Ensuring the accuracy of data will increase success. In addition, thorough exploration of the root cause of problems will lead to proper solutions that prohibit repeat offenses. Companies will take the time to communicate, educate, and implement real changes that are tracked and closely managed by leadership teams. Focusing on the development of a solid, repeatable process provides a safeguard for future project success.

As the system works to develop continuous improvement accountability, businesses move from addressing necessary issues and small initiatives to tackling larger, organizational enhancement plans.
Company-Wide Communication
Compliance Does Not Require Certification
It’s important to know that compliance does not require certification from a third party.
Small businesses often choose compliance without taking the full step to certification simply due to the added cost of the third-party audit. Others may choose to forego certification due to company policy, customer-led audit, or the satisfaction of regulations by compliance only.
So why pursue full-blown certification? Having a certification body check out an EMS shows due diligence of responsibility to the environment and opens the doors for the contracts that do require certification. Additionally, certification sets a deadline for EMS projects which can motivate teams to complete tasks and implement the changes necessary for improvement.
In a global economy that is moving quickly toward more stringent regulations, certification proves that companies are leading the pack when it comes to environmental excellence.
A Results Driven Improvement System
Working toward ISO 14001 compliance and certification requires organizations to follow a structured process to develop an effective EMS. With specific touch points and by following a process approach, organizations will find a results-driven improvement system.
Process Approach and Impact
This process approach is key to compliance and certification to ISO 14001. A process-based EMS is used as a tool to provide consistency and set expectations related to environmental impact and is the most effective method of addressing and managing risks.
As with many ISO standards, 14001 requires companies to implement a process approach to the development of their EMS. The term “process” refers to actions and activities that can be consistently repeated to produce a change to a product or service based on a series of inputs. “Inputs” are any element or information that feeds the process. The “process approach” is when all of these aspects are managed together as they work toward an end goal. Through this approach, each process will produce “outputs,” which can relate to both deliverables and undesirable factors. For example, in environmental systems, waste, and pollution are considered undesirable outputs of a process.

Context and Scope of the Organization
Within ISO 14001, organizations must define the context in which they will pursue compliance and certification. Both external and internal factors that contribute to the company’s ability to achieve its goals will be evaluated. Any part or function that may affect the company’s objectives must be considered. The EMS can apply to the entirety of an organization, or specific processes, facilities, or deliverables.
Once these factors have been determined, the company must then develop an understanding of the expectations of all interested parties, including customers, stakeholders, employees, and the communities surrounding their facilities.
Both context and interested parties combine to help define the scope of the EMS, or the functions of the business that will be included in the development of the system. Products and services, physical locations, activities, and employees are all considerations when evaluating the scope of a project.
Environmental Aspects
Specific to ISO 14001, organizations need to identify the environmental factors of their business their Environmental Management System will address. In addition, they must identify the potential impacts of those factors, and the management of those factors.
By identifying the environmental aspects, companies will have to determine the difference between the activities they perform (i.e., the production process itself), the services that support their activities (i.e., machinery, boilers, maintenance systems), and the product they deliver. Regarding products, environmental aspects may be found in the packaging or in the life cycle and recyclability of the product.
Organizations must establish procedures for identifying the various factors of their business that make an impact on the environment.

Keeping Records
Keeping a record of these factors can be helpful as companies move past initial implementation and on to continuous improvement, and planning for new or modified activities, services, and products.
There are obvious core manufacturing or service activities that are easy to define within the scope of the EMS. Companies must also consider offices, systems, parking lots, supplier activities – anything that could have an environmental impact. Utilizing employees from various departments within an organization can help with a thorough and complete evaluation of a company’s environmental factors.
Once a list has been established, exploration of environmental factors can begin. Companies will divide factors into direct and indirect segments, with direct factors defined as those sourced from and controlled by the organization.
Indirect factors are often those associated with non-industrial organizations or aspects that are driven by external sources (such as subcontractor waste management or supplier-controlled inputs). After the division of factors, the company will evaluate how those factors affect the environment.
Evaluating the significance of each environmental aspect is what will help set the framework for the structure of a company’s EMS. Organizations should not try to tackle every topic identified by their exploration team. They should focus on the aspects that will have the most significant impact.
Significance is determined by several factors, including the potential to cause environmental harm, the size and frequency of the problem, the importance to the team, customers, and other stakeholders in the organization, and relevant contractual requirements and legislation.
This evaluation is unique to each organization implementing an EMS and should be explored with the company’s unique goals in mind.
Finally, organizations will work to develop a plan to manage the significant environmental impacts they have defined through a strategic EMS. All significant factors should be brought under control, and plans put in place that are appropriately related to the risk and impact of the factor. Factors can be controlled by a responsible person, training plan, procedure, checklist, or maintenance schedule.

Often, companies add unnecessary complexity to their EMS. By identifying the key environmental aspects with the highest level of potential impact at the very beginning of the process, organizations can utilize their EMS to realize benefits and improve their business.

Integrating ISO 14001 and ISO 9001
With a base of requirements closely tied to those found in the flagship ISO 9001 standards, ISO 14001 allows companies to capitalize on existing compliance by utilizing the following processes:
- Policy creation and dissemination
- Objectives creation and dissemination
- Competence, training, and awareness processes
- Communication of management system information
- Control of system documentation
- Control of records
- Control of non-conformities
- Corrective action and preventive action
- Internal audit
- Management review
Utilize Existing Processes
Companies will be tasked with updating their existing processes to include the information pertinent to the environmental aspects their EMS will address. Utilizing the existing processes allows for easy integration of the two standards.
Where companies will find additional work in the processes specific to environmental regulation and excellence, namely:
- Environmental policy (including the goals and guidelines for proper implementation and maintenance)
- Legal requirements (with processes to ensure identification and compliance)
- Environmental aspects (as defined above in the details section)
- Objectives, targets, and programs (specifically related to the company’s environmental goals)
Overall the benefit and easy integration to ISO 9001 make ISO 14001 a natural second step for many organizations seeking to add to their list of credentials. At Core Business Solutions, we’re happy to provide the support you need, whether adding to an existing management system or developing a brand new environmentally-focused initiative.
“If you don’t believe that one person can make a difference, then you haven’t been in bed with a mosquito.” Anita Roddick
Reach out to us and let us know how we can help you grow at info@thecoresolution.com.
About Scott Dawson
Since 2010, Scott Dawson, President of Core Business Solutions, has been an active voting member of the U.S. Technical Advisory Group (TAG) to ISO Technical Committee 176 (TC 176). TAG 176 members meet to discuss and develop U.S. positions for Quality Management standards, including ISO 9001:2015, which will be revised in 2025.




